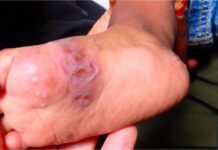
This factsheet highlights some common side effects associated with the Johnson and Johnson COVID-19 vaccine.
The Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine is a single-dose vaccine and according to the US CDC the following are possible side effects that recipients of the jab may experience:
In your arm where you got the shot, you may experience:
- Pain
- Redness
- Swelling
What you may experience in throughout your body after vaccination
- Tiredness
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Chills
- Fever
- Nausea
WHO recommendation
The WHO Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunisation has issued updated interim recommendations (June 25) for the use of the Janssen Ad26.CoV2.S vaccine against COVID-19.
The interim recommendations provided guidance on several issues including people advised not to take the vaccine.
They include;
- Individuals with a history of anaphylaxis should not take it.
- Anyone with a body temperature over 38.5ºC should postpone vaccination until they no longer have a fever.
- The vaccine is not recommended for persons younger than 18 years of age pending the results of further studies in that age group.
How efficacious is the vaccine?
According to the WHO, 28 days after inoculation Janssen Ad26.CoV2.S was found to have an efficacy of 85.4% against severe disease and 93.1 % against hospitalization.
A single dose of Janssen Ad26.COV2.S was found in clinical trials to have an efficacy of 66.9% against symptomatic moderate and severe SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The Janssen vaccine is considered safe and effective at protecting people from the extremely serious risks of COVID-19, including death, hospitalization and severe disease.
Culled from GhanaFact
==================================================================================
FACTSHEET: Will delay in receiving 2nd dose of COVID-19 vaccine affect it’s effectiveness?

According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Africa has the world’s lowest COVID-19 vaccination rate. The delay in vaccination has become a major concern as some recipients of the first dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine, continue to wait for the second dose well beyond the recommended wait period.
Research has shown the AstraZeneca jab generates the strongest immune response when given 12 weeks apart. So, will any further delay affect the effectiveness of the vaccine?
What happens if your second dose delay?
“There is no complication if you go beyond your time for the second dose,” Programme Manager, Expanded Programme on Immunization of the Ghana Health Service (GHS), Dr Kwame Amponsa-Achiano, told GhanaFact.
“For vaccines, what we know scientifically is that we have a minimum interval, we also have an optimum interval but we do not have a maximum interval,” he said.
Explaining this further, Dr Amponsa-Achiano said “the first dose gives some protection for some time then the protection starts reducing. The best time as of now to give the second dose is around 12 weeks or soon after. If it goes beyond, it does not mean that there is any complication, it only tells us that if we wait too long the protection will go down not as if it’s even going to zero.”
“We do know that antibody levels slowly wane for up to 6 months after the first dose is given so we do not expect a sudden drop in protection after 12 weeks. It is very important to get the second dose to get maximum protection over time,” the WHO told GhanaFact when contacted via the Africa Infodemic Response Alliance (AIRA) secretariat.
There should be no complications due to a delay in getting the second dose, but being fully vaccinated with two doses of the AstraZeneca vaccines will provide greater protection against the virus, the WHO emphasized.
“The reason why we say 12 weeks is that that is the duration of time for us to have data. Most data on AstraZeneca in terms of the antibodies and everything is coming from the UK. And most people in the UK because they have supplies, didn’t have to go beyond the 12 or 16 weeks without getting a second dose. That’s where the data ends,” a Research Fellow in the Department of Health Policy and Management at New York University’s School of Global Public Health Nana Kofi Quakyi explains to GhanaFact.
According to him, figuring out the effectiveness of the single-dose beyond the 12 weeks to 16 weeks should be a follow-up study for any Public Health Service facing such challenges.
“The issue is that we don’t know specifically what those timelines are and because we don’t know, the moral obligation on the public health service in any country that is facing that problem is to do a follow-up study. So, all people or some number of them who are missing that 12-week should be in a study,” he said.
Ghana is expected to take delivery of 1.2 million doses of Pfizer from the US through COVAX, a channel established to ensure even distribution of the COVID-19 vaccines and about 17 million doses of Johnson and Johnson in August.
Source: GhanaFact
=============================================================================
FACTSHEET: Is it safe to be mixing COVID-19 vaccines?

Is it safe for countries dealing with COVID-19 vaccine shortages to consider mixing the vaccines to inoculate their citizens from the disease? Countries like Canada, Germany, France, Sweden, Finland, Denmark and Norway are currently mixing vaccines – with either the AstraZeneca-Oxford, Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna shots being administered interchangeably in certain situations.
Africa is facing a fast-surging third wave of COVID-19 pandemic, and vaccines are increasingly scarce, 47 of Africa’s 54 countries—nearly 90%—are set to miss the September target of vaccinating 10% of their people unless Africa receives 225 million more doses.
So, is mixing COVID-19 vaccines an option?
WHO position
“WHO has not issued a clear recommendation on the use of mixed schedules. We are waiting for additional data to make a firm recommendation,” the WHO told GhanaFact when contacted via the Africa Infodemic Response Alliance (AIRA) secretariat.
Here is an outline of the progress made by the WHO in researching mixing and matching:
- On 15th June 2021, WHO’s Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunisation (SAGE) updated its interim recommendations on the Pfizer vaccine to give a permissive recommendation to use the Pfizer vaccine as a second dose following a first dose with the AstraZeneca vaccine if a second dose of AstraZeneca vaccine is not available due to supply constraints or other concerns, the team also told GhanaFact.
- A clinical trial led by the University of Oxford, in the UK is currently ongoing to investigate mixing the regimen of the AstraZeneca vaccine and the Pfizer vaccine.
- This trial was recently expanded to include the Moderna and Novovax vaccines. CEPI, which leads the R&D aspect of the COVAX facility, announced on May 26 that it will fund an expansion of the clinical trials.
Safety and efficacy of mixing and matching vaccines
The WHO Africa Infodemic Response Alliance told GhanaFact that;
- “Preliminary findings from the University of Oxford trial showed that people who received the Astra Zeneca vaccine for their first dose, followed by the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine as the second dose had a higher likelihood of fever and other typical mild side effects than if they had stayed with 2 doses of the Astra Zeneca vaccine.”
These side effects lasted on average a few days and no hospitalizations occurred. This study was done among people aged 50 and over.
Meanwhile, on July 12, 2021, World Health Organization Chief Scientist -Dr Soumya Swaminathan during an online briefing cautioned individuals who are thinking of mixing and matching vaccines without following guidance from public health authorities.
“Really want to caution folks because there is a tendency now for people in countries with enough availability of vaccine to voluntarily start thinking about an additional dose. There are people who are thinking about mixing and matching. We received a lot queries from people who say they have taken one and they are planning to take another one. It is a little bit of dangerous trend here, where people are in a data-free evidence-free zone as far as mix and match, there is limited data on mix and match.”
There are still studies being conducted into mixing and matching and more research and data would be needed to support the safety as yet. However, the tolerability results of some recipients(mix and match) during clinical trials conducted so far show there is no harm in mixing and matching COVID-19 vaccines right now and it helped in boosting the immune response.
“If they are going to do mixing and matching [in Ghana], all those people have to be given oral informed consent about the information we know about mixing and matching. And that decision has to be made with equally serious follow-up.” A Research Fellow in the Department of Health Policy and Management at New York University’s School of Global Public Health, Nana Kofi Quakyi told GhanaFact in an interview.
Culled from Ghana Fact
================================================================================
FACT-CHECK: Virologist Luc Montagnier did NOT say all vaccinated people will die within 2 years- moreover, the claim is FALSE

Claim: All vaccinated people will die within 2 years
Source: WhatsApp Message
Verdict: FALSE
Researched Gifty Tracy Aminu
A widely circulated message on WhatsApp in Ghana claims all people vaccinated against COVID-19 “will die within 2 years” and this is being attributed to French virologist and joint recipient of the 2008 Noble Prize in Medicine, Luc Montagnier.
“It’s an enormous mistake, isn’t it? A scientific error as well as a medical error. It is an unacceptable mistake,” he is quoted in the WhatsApp message to have said in relation to the global vaccination effort to curb the spread of COVID-19.

This fact-check report will seek to verify two claims.
- Whether Luc Montagnier actually said, “all vaccinated people will die within two years.”
- Whether COVID-19 vaccines create new variants.
Did Luc Montagnier say- “all vaccinated people will die within 2 years?
GhanaFact has found a viral video interview granted by the French virologist, which is being used to confirm the viral claims. The video which is 2 minutes 18 seconds long has a “RAIR Foundation USA” logo embossed on it.
Even though the interview was conducted in French, the video comes with English subtitles for non-French speakers. But nowhere in the interview does Luc Montagnier make the claim that “all vaccinated people will die within 2 years” as being attributed to him. The complete interview can be seen here.
Moreover, the World Health Organization has said COVID-19 vaccines just like any other vaccines used in the past are safe and effective. “Vaccine safety is one of the highest priorities, and we’re working closely with national authorities to develop and implement standards to ensure that COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective,” the WHO has said.
“COVID-19 vaccines substantially reduce the risk of people getting sick and dying of the virus. They are a crucial tool in ending the pandemic. There is absolutely no poison in COVID-19 vaccines and over 2.3 billion doses have been given all around the world so far. COVID-19 vaccines could well save your life, so when you get the chance, please get the vaccine,” the WHO Africa Infodemic Response Alliance secretariat told GhanaFact.
Verdict
The claim that all vaccinated people will die within two years is FALSE.
Source: GhanaFact
=========================================================================
FACT-CHECK: Do you lose your innate immune system after taking a COVID-19 vaccine?

Claim: 2 COVID-19 vaccine conspiracy theories
Source: WhatsApp video
Verdict: 2 FALSE
A video clip that has been tagged by WhatsApp as “forwarded many times” is promoting a host of COVID-19 vaccine conspiracy theories.
The clip shows an American television producer and CEO of the anti-vaccination group: “Informed Consent Action Network,” Del Bigtree making unfounded claims about the coronavirus pandemic and why people should not take the COVID-19 vaccines.

The 17 minutes and 31seconds long video which is captioned: “Vaccine Disaster Ahead…” also amplifies claims made by an independent researcher and COVID-19 anti-vaxxer, Geert Vanden Bossche.
With support from the WHO Africa Infodemic Response Alliance (AIRA), GhanaFact has flagged two claims made in the video as FALSE.
Claim 1
“Fact is, these long live antibodies which have high specificity of course for the virus, they out-compete our natural antibodies because the natural antibodies have a very broad spectrum that has a low affinity. The specific antibodies will continue to out-compete your natural antibodies and that is a huge problem. These natural antibodies, provide us with broad protection…” Geert Vanden Bossche partly said.
Fact-check
“Vaccination is a simple, safe, and effective way of protecting people against harmful diseases before they come into contact with them. It uses your body’s natural defenses to build resistance to specific infections and makes your immune system stronger. It produces antibodies. Antibodies are proteins produced naturally by the immune system to fight disease.” The World Health Organization (WHO) has said.
It is important to note that, COVID-19 vaccines are not the first kind to be introduced for protection against infectious disease. According to the WHO, “there are vaccines available to protect against at least 20 diseases, such as diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, influenza, and measles. Together, these vaccines save the lives of up to 3 million people every year.”
Vaccines train your immune system to create antibodies, just as it does when it’s exposed to a disease. However, because vaccines contain only killed or weakened forms of germs like viruses or bacteria, they do not cause the disease or put you at risk of its complications.
Verdict
The claim that vaccines will cause some specific antibodies to outcompete one’s natural antibodies is FALSE.
Claim 2
“It is a global problem of making this virus increasingly infectious because we live it all the time a chance and opportunity to escape with the immune system and to drive this up to a level that the virus is so infectious that we can even no longer control it.” Geert Vanden Bossche partly said
Fact-check
“COVID-19 vaccines do not make the virus more infectious.” The WHO Africa Infodemic Response Alliance (AIRA) said in response to the claim.
According to the WHO, vaccination is a key part of the solution to stop the spread of the virus and to stop new variants emerging as it spreads, along with existing public health measures like mask-wearing, hand cleaning and physical distancing.
COVID-19 vaccines provide protection against the disease by helping the body developing an immune response. Developing immunity through vaccination means there is a reduced risk of developing the illness and its consequences.
This immunity helps you fight the virus if exposed. Getting vaccinated may also protect people around you because if you are protected from getting infected and from disease, you are less likely to infect someone else, they added.
Verdict
Therefore, the claim that COVID-19 vaccines would cause the virus to be more infectious is FALSE.
Source: GhanaFact
===================================================================================
FACT-CHECK: Claim that some COVID-19 vaccines are less effective than previously announced is FALSE

Claim: Five COVID-19 vaccines have lower efficacy than previously announced
Source: Facebook post
Verdict: FALSE
A widely shared Facebook post is claiming the effectiveness of five COVID-19 vaccines in protecting recipients from getting severely ill, even if they are infected with the coronavirus, is lower than previously announced.
The Facebook post that has generated about 4,700 interactions is alleging that the public was deceived about the efficacy of some of the COVID-19 vaccines.

“We have been lied to, again! The effectiveness is not 70-90% like they claimed it to be, but much lower.” The post said and further claimed that some vaccines had less than 2% efficacy. They include: “1.3% for the AstraZeneca, 1.2% for the Moderna, 1.2% for the J&J, 0.93% for the Gamaleya, and 0.84% for the Pfizer.”
Fact-Check
| VACCINES | VERIFIED EFFICACY |
| AstraZeneca | 70% overall |
| Moderna | 94.1% |
| Johnson & Johnson | 66.3% |
| Gamaley or Sputnik V | 91.6% |
| Pfizer | 95% |
“Based on evidence from clinical trials, the Moderna vaccine was 94.1% effective at preventing laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 illness in people who received two doses who had no evidence of being previously infected.” The Center for Disease Control and Prevention has said.
The vaccine appears to have high effectiveness in clinical trials (efficacy) among people of diverse age, sex, race, and ethnicity categories and among persons with underlying medical conditions.
In the case of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine, the CDC stated that “based on evidence from clinical trials in people aged 16 years and older, the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine was 95% effective at preventing laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 illness in people without evidence of previous infection.”
The Johnson and Johnson COVID-19 vaccine, which is just a single dose shot, has 66.3% effectiveness in clinical trials (efficacy) at preventing laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 illness in people who had no evidence of prior infection. People had the most protection 2 weeks after getting vaccinated.
The US Center for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drugs Administration said “the J&J/Janssen COVID-19 Vaccine is recommended for people aged 18 years and older, however, women younger than 50 years old should especially be aware of the rare risk of blood clots with low platelets after vaccination.”
The AstraZeneca/Oxford COVID-19 vaccine manufacturers gave a breakdown of the performance of the vaccine in an update on March 25, 2021. “76% vaccine efficacy against symptomatic COVID-19, 100% efficacy against severe or critical disease and hospitalization and 85% efficacy against symptomatic COVID-19 in participants aged 65 years and over.”
Despite the rare occurrence of reports of blood clots among some recipients of the AstraZeneca vaccine, the World Health Organization maintains that the “AstraZeneca vaccine is safe and effective at protecting people from the extremely serious risks of COVID-19, including death, hospitalization, and severe disease.”
The Gamaaleya COVID-19 vaccine is the same as the Sputnik V. “Sputnik V is one of the three vaccines in the world with efficacy of over 90%. The Vaccine’s efficacy is confirmed at 91.6% based on the analysis of data on 19,866 volunteers, who received both the first and second doses of the Sputnik V vaccine or placebo at the final control point of 78 confirmed COVID-19 cases,” the manufacturers said.
They further highlighted that “analysis of data from 3.8 million vaccinated persons in Russia Sputnik V demonstrates 97.6% efficacy.”
PolitiFact, a non-partisan fact-checking project by Poynter Institute in St. Petersburg, Florida, has flagged a similar claim on Instagram to be FALSE.
Verdict
The claim that some COVID-19 vaccines are less effective than previously advertised is FALSE.
Source: GhanaFact
====================================================================================
FALSE: COVID-19 vaccines do NOT contain microchips!

Claim: COVID-19 vaccines contain microchips
Source: WhatsApp Video
Verdict: FALSE
A 2 minutes 10 seconds long video showing 4 people who claim the spot of their COVID-19 injection now reacts positively to magnetic objects is being widely shared on WhatsApp.
The video which has “TimTruth.com” embossed on the top right-hand corner also comes with a subtitle that claims, “more people catching on to their jabs being magnetic” and questions whether recipients of COVID-19 vaccines are being “microchipped.”

A voice-over narration of what was captured encourages the public to widely share the video so it could be independently investigated. “People are finding that they can put a magnet at where they got vaccinated and it will stick. I found eleven examples of this. I am scouring the internet; I found these eleven examples and I wanted to put together an ultimate compilation. So, check this out.” The person partly said.
The video showed multiple persons sticking some objects to where they claimed to have received their jabs and according to one of them who received the Pfizer vaccine, the magnetic reaction is true.
Fact-check
Experts at Meedan’s Health Desk, a group of public health scientists working to tackle medical misinformation online, said “the vaccine is not known to contain any metals or cause any response to magnetic fields. Only certain metals can trigger magnetic reactions, and the vaccine does not contain any metals at all. That means it can’t cause a magnetic response when it’s injected.”
The Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine’s list of ingredients includes mRNA, lipids, potassium chloride, monobasic potassium phosphate, sodium chloride, dibasic sodium phosphate dihydrate, and sucrose.
“The amount of metal that would need to be in a vaccine for it to attract a magnet is much more substantial than the amounts that could be present in a vaccine’s small dose.” Experts at Meedan’s Health Desk emphasized.
“None of the COVID-19 vaccines contain software or microchips. They cannot track people”, the Department of health-Australia has stated.
According to the State of Indiana, USA: “the vaccines do not contain microchips or any other sort of device. It is impossible for a microchip to be placed in a vaccine.”
Other credible fact-checkers including the Reuters Fact Check, US TODAY Fact Check and Australia Associated Press FactCheck have flagged similar claims as FALSE.
Verdict
The claim that the COVID-19 vaccines contain microchips is FALSE.
Source: GhanaFact